Application Dictionary Layers
This documentation is started by Red1. You may discuss further improvements at Talk:ADempiere Rapid Development
Motivation
- Today's needs are on the fast-track. Users want an ERP within 6 months instead of 18 months.
- ERP apps have bloated to become everything to everybody and one size fits all.
- Quality large scale implementations can no longer be done by a single expert and requires open sharing among all parties.
- Speciliasation by differentiated contributors lower total cost of ownership for paying users.
ADempiere As An Application Framework
Since ADempiere's Application Dictionary resolves the need to touch sourcecode or base software to a minimum, and allow changes to be made rapidly and conveniently to not only the look and feel of the Data Model but also the Business Model, we can call it an Application Framework.
An Application Framework basically helps you to develop an application without starting from scratch. ADempiere already has the look and feel and many accessories resolved to work stably and marvelously. Such features and accessories need not be coded further in a fresh software design.
A new software to be created can just introduce its DataModel as Tables and Columns arranged within Windows and attached to Menu Trees.
Each User login will be controlled by its allowed Role or Roles to access or not to access certain Menu of Windows or Processes or Reports.
Application Modelling
ADempiere acts as a horizontal application where other or new vertical applications can reuse or sit on it.
Before a new application is introduced, it need to be designed and modelled accordingly that fits onto the ADempiere Framework.
To design a new application on top of ADempiere is perhaps the hardest or biggest portion of the cost of an application development
- Any application design is hard. The bigger it is the harder it is. The more modules to integrate, the challenge increases exponentially.
- But spend enough time planning it (50%), and enough time designing it (90%), the coding part is only 10%.
- The resulting work to code or migrate the system to is simple.
There are various migration tools to do the final integration of legacy application data or model into ADempiere. Among them are the:
- Import Loaders (incumbent model)
- ADCK (XML2AD enhanced model by Trifon T.)
- 2Pack (XML2AD enhanced model by Robert Klein - standard for migrating own apps)
- Migration Scripts (standard for new apps)
- OSGI Module deployment (latest version is OSGI HengSin)
The importance at the systems design stage is to study the inherent ADempiere model and framework well enough to reuse them to the maximum and to avoid work redundancy and later complications.
A succesfully introduced or migrated vertical application will enjoy not only the incumbent multiple rich interfaces and application engine, but also a quantum leap into the open source services market.
Intending application developers must realign their Software Business Model to an entirely new one.
Data Modeling
NOTE that where the word 'must' is used would mean that it is mandatory and non-negotiable for successful implementation.
The word 'should' would mean that it is optional but encouraged for maintainability and scalability of the system.
SQL scripts for each data model can be executed first in the Database. Then the AD's Table and Column can bring in those created tables into the Application Dictionary.
Each table must have the compulsory fields for model persistence and management within the ADempiere Framework:
- AD_Client_ID: Signifies the highest level and distinct identity that owns all organizational activity.
- AD_Org_ID: Signifies sub-levels below and within the Client.
- Created: Signifies the timestamp for each record in this table at the time of its creation.
- CreatedBy: Signifies the User_ID that creates the record.
- Updated: Signifies the timestamp for each record's last update.
- UpdatedBy: Signifies the User_ID that last updated the record.
- IsActive: Signifies whether the record is active or not.
Each table name must have its primary key as its respective table name plus underscore ID. For example, a new table 'Cigars' will have its PK as 'Cigars_ID'. Any deviation from this naming convention will result in a failed model during execution.
Each table should have a 'value' field for search key purposes. In short, 'value' is another reserved name in ADempiere's table modeling.
Entity Relationships between tables can be established by having fields that follow the table ID convention. For example, another table 'Cigar Smokers' will have 'Cigar_ID', indicating it is a Foreign Key to the 'Cigar' table. This represents a loosely stated relationship.
- The presentation of an entity relationship is managed within the Window, Tab & Field setup. A sub-tab will have its parent key linkage specified, tightly defining the relationship but only during Window displays.
- The apparent master-detail relationship through this PK-FK (primary key - foreign key) statement is enforced during data entry, where each detail line possesses the parent's ID or primary key.
- Additionally, you can apply constraints within the database constraint settings to prevent the deletion of a parent if a child record still exists
Master Detail table naming should be that the Detail table has suffix 'Line' added to its name taken from the Master table. For example a 'Cigar' table can be a master table with a detail table as 'CigarLine'.
Figure 1 - The DataModel is integrated to the Application Dictionary
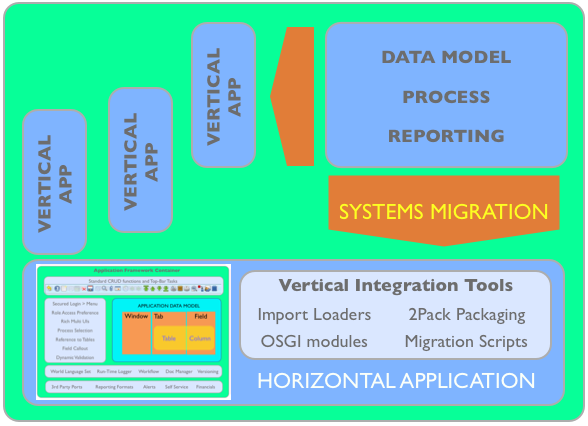
Figure 2 - Any vertical application can be incorporated and reuse standard utilities
Document Modeling
Sequence Numbering
Report Modeling
- The Reporting Engine in ADempiere (fully inherited from Compiere) is truly on the fly and hot configurable.
- In any window table with records you can click on the Report icon.
- Take note of the pop-up report viewer displaying the selected single record.
- Click on the Search icon within the viewer.
- Simply click "OK" to select all records.
- Observe that all records are generated.
- Utilize an Advanced Search to access any desired report cube.
- Your advanced preference settings can be saved for future use.
- Refer to this sample in E-ticketing#Reporting_On_The_Fly.
- You can reformat the fields and its arrangement easily via the PrintFormat
Report ToolsBox
(refer to Figure 3)
- In the same pop up window, select the ToolsBox to zoom into the PrintFormat window
- Click on the Display Order tab
- Select those fields you do not want to appear. You can move them around in your prefered order.
- Click on the back arrow key to remove them for this report
- You can then save your new report for later use.
- Click on the Field Format tab
- Additional functions can be implemented, such as calculating the total or running sum of a field with an amount or countable value.
- When you exit and refresh, the report changes are reflected.
- All changes are automatically saved in your new report definition.
- Your customized configurations can be transferred either through Log Migration scripts (preferred) or 2Pack package management.
Figure 3 - PrintFormat engine assist in configuring reports easily 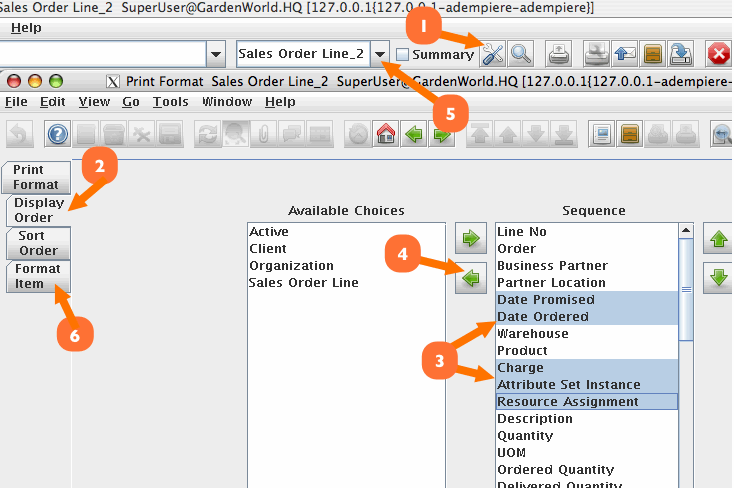
Advanced Search
- An on-the-fly Advanced Search engine is readily available for filtering results in both display windows and reporting formats.
- The boolean rules provide the flexibility to filter based on any imaginable set of information.
- This feature significantly reduces the necessity to develop additional engines or tools for generating specific ranges of reports.
(refer to Figure 4)
- In the Report Viewer, click on the Search icon
- Select the items and boolean rules to values needed.
- Save it with a nice name to recall whenever you want the same advanced search
Figure 4 -Advanced search filter can be saved and recalled 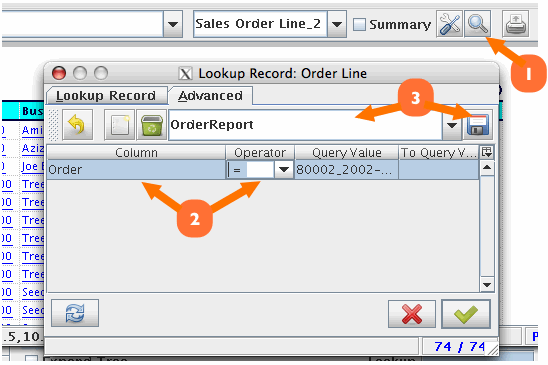
Process Modeling
At the Tab Level
- The AD Framework enables any field in the Table & Column model to have a Callout.
- A Callout triggers an action when an OnChange event occurs within the field.
- The action can involve reading and calculating a new value for any field in the Tab.
- Calculations may access any table or modify its value within the Database.
- Callouts can be implemented in Java code, either compiled into source or in metadata form without altering the source.
- Metadata Callout supports JSR223 scripting options such as Python, Beanshell, Groovy, and potentially Ruby,
At The Document Level
- There is a button field that can spawn a process written in SQL or Java Code
- The process can determine an elaborate process:
- Accounts Posting
- Workflow Management
- Records Change
- At the end of the process, the button may change its state and the Tab record state is changed.
A Model goes through various Controller Process that automate work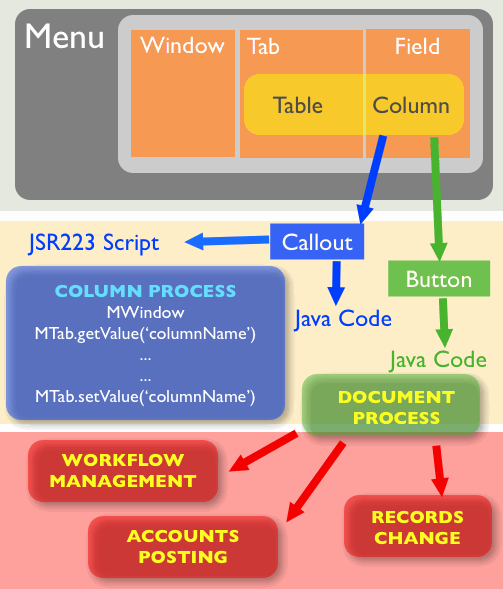
Deployment
Testing Framework
Maintenance
See Also
- Top Menu Views
- Software Business Model
- E-ticketing
- EDIFACT as a real extension using more complex programming but simple data model change.
- Callout and Script Callout